Why Does My Old Injury Still Hurt?
March 29, 2024
If you hurt yourself years ago, through some form of exercise or by pushing your body too far, but find yourself thinking, “Why does my old injury still hurt?”, your injury probably healed poorly. Scar tissue is probably the culprit behind chronic pain of your old injury, and it can be addressed by a massage therapist skilled in assessment and treatment. In this blog post, I’ll go over how scar tissue causes chronic pain, and what can be done about it.
What Causes Chronic Pain in Old Injuries?
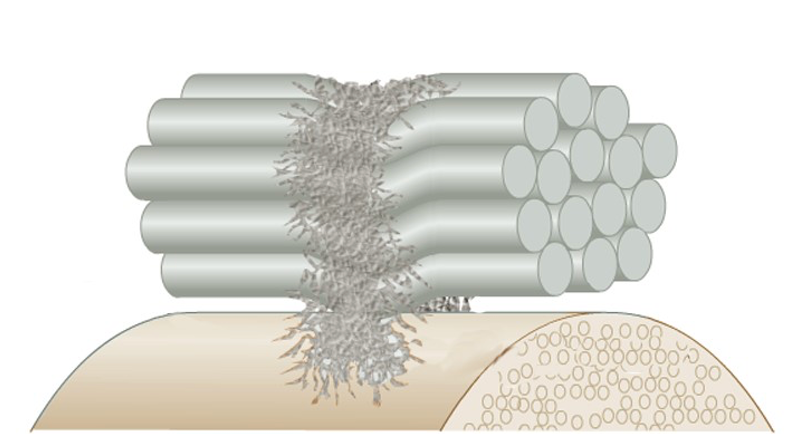
First, you have to understand the different types of scar tissue. Scar tissue forms whenever there is an injury in your body. Good scar tissue forms approximately in the right places and allows you to heal without pain. Bad scar tissue, called adhesive scar tissue, is weak and forms in the wrong places.
In most cases of chronic pain in the body, the culprit is adhesive scar tissue, whether the pain is in the lower back, the neck, the shoulders, thighs, knees, calves, feet, ankles, or anywhere else in your body. When scar tissue forms randomly, things stick together inappropriately, and pain usually results. The scar tissue is like glue poured into the wrong places, causing body parts that should move independently to stick together. Movement that pulls on, stretches, or compresses the area where adhesive scar tissue has formed causes pain.
Because the injury has healed poorly, you are probably re-tearing and injuring yourself over and over again, even if it’s not to the same degree as your original injury.
What Happens When an Old Injury Doesn’t Heal Properly?
If an injury in your shoulder forms adhesive scar tissue, pain in the shoulder or arm results. Over time, without any therapeutic intervention, the body adjusts to this pain, and you subconsciously begin to use that part of your body less and less. You start avoiding the movements that will cause pain, your range of movement slowly diminishes, and the atrophy process begins. Atrophy means that you get weaker and weaker as you use your muscles less.
Can a Massage Therapist Find the Source of the Pain and Eliminate It?
If your therapist is skilled in assessing and treating injuries, they can. Using a variety of assessment tests, they can identify the source of your pain, which is frequently adhesive scar tissue in a particular muscle, tendon, or ligament. Once they find the source, they can usually perform a successful treatment, unless the injury is very severe. They would then refer you to another professional to get it addressed.
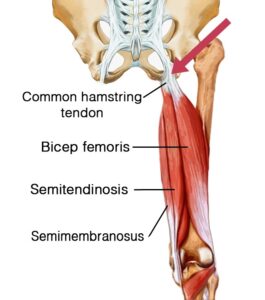

For example, to find an injured hamstring tendon, your massage therapist would perform a few simple hands-on tests. Then, they would put their fingers on the tendon to confirm that it’s painful. Successful treatment can then be administered. Once all of the adhesive scar tissue has been eliminated by manual therapy, full movement is restored, and the chronic pain is gone. After that, normal strength can be rebuilt through a series of rehabilitative exercises.
I just saw a bodybuilder client who had a shoulder problem for over ten years. After doing a series of physical tests on his shoulder, I found that he was so strong that I had to use all of my strength and then some. In one test, he was so weak that I could overpower him with one hand. There was no pain until I made him work really hard on that test. It’s the one in this photo.

When someone is very weak in a single muscle, it usually means that some part of that muscle group is injured. Every muscle group, or unit, has two parts: the muscle and the tendon that attaches the muscle to the bone. Because no one had been able to figure his injury out in ten years, his body had found a simple solution: just avoid using that muscle because it causes too much pain. While he was subconsciously avoiding the pain, he was losing strength, and his muscles were atrophying. That’s dangerous because if he suddenly had to catch himself while falling, he would have hurt himself even more.
How Do I Find a Massage Therapist Who Can Treat My Old Injury?
Try searching for “orthopedic manual therapy,” “friction therapy,” or “chronic pain.” Don’t be afraid to call or email a business to ask if they offer this type of treatment. And if you’re in the Boston, MA area, I have been treating chronic pain for decades and am also available by appointment.
If you’re not in the Boston area, I can still help by conducting a remote evaluation session, where I walk you through a series of assessment tests. You’ll need either your current massage therapist or someone I can direct to perform the assessment tests. You can also email me or call my office to see if this is a good fit for you or ask any questions you might have beforehand.
If you are experiencing chronic pain and live in the Boston area, schedule an appointment or a complimentary 10-15 minute phone consultation.
Schedule an Appointment or Call →
Ben E. Benjamin holds a Ph.D. in Sports Medicine and was the founder and President of the Muscular Therapy Institute in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He is the author of dozens of articles on working with injuries and chronic pain as well as the widely used books in the field, Are You Tense?, Exercise Without Injury and Listen To Your Pain: The Active Person’s Guide to Understanding, Identifying and Treating Pain and Injury. Dr. Benjamin has been in private practice for over 50 years and teaches therapists throughout the country.
Why Does My Old Injury Still Hurt FAQs:
- What causes chronic pain in old injuries?
When an injury heals poorly, it forms bad scar tissue, called adhesive scar tissue, which is weak and vulnerable to re-tearing and re-injury. This causes your old injury to still hurt, even years later.
- What happens when an old injury doesn’t heal properly?
Your body starts to adjust to the pain by avoiding any motion that causes it, and your muscles start to atrophy, or weaken.
- Can a massage therapist find the source of the pain and eliminate it?
Yes, if your massage therapist is skilled at assessing and treating injuries.
- How do I find a massage therapist who can treat my old injury?
Try searching for a massage therapist who specializes in “orthopedic manual therapy,” “friction therapy,” or “chronic pain.” You can also see me for an in-person appointment in the Boston, MA area or for a remote evaluation.
Related Posts
Can Massage Help Pain that Travels? Cambridge MA
Question: Why does an injury to the neck cause pain that travels to the arm and hand? Answer: Referred Pain Pain that travels in your body is called Referred Pain. This phenomenon means the injury is in one place, and the pain is in another. Understanding this phenomenon helps you better understand your body’s responses […]

Can Massage Therapy Help Lower Back Pain Cambridge, MA?
Lower back pain is experienced by at least 50 million people each year in the United States alone. My own severe back pain when I was a teenager is what led me into this field. Back pain is often a debilitating, terrible experience. But it can also be annoying and limiting. I’ve treated hundreds of […]

Massage Therapy for Chronic Neck Pain Near Cambridge, MA
Question: What’s the most common cause of chronic neck pain? Answer: Ligament sprains The Causes of Pain in Your Neck For many reasons, your neck can be painful, but most people are unaware of the most common cause of chronic neck pain. Sprained or severely injured muscles can cause pain in the neck, but muscles […]
Can a Massage Therapist Fix a Frozen Shoulder in Cambridge, MA
Question: Does a frozen shoulder always go away with time? Answer: Often no. The Causes of Frozen Shoulder A frozen shoulder can be incredibly painful. The pain originates in the shoulder joint. A joint is formed where any two bones meet. It’s the enclosed space between your upper arm bone, the humerus, which is […]

Can Massage Therapy Help Hamstring Pain Near Cambridge, MA
Question: Do you think a similar pain in the back of the thigh while running can be attributed to a hamstring injury or a lower back injury? True or False? Answer: True Hamstring Anatomy You have three hamstring muscles in the back of your thigh. Every muscle has a tendon that attaches it to […]
